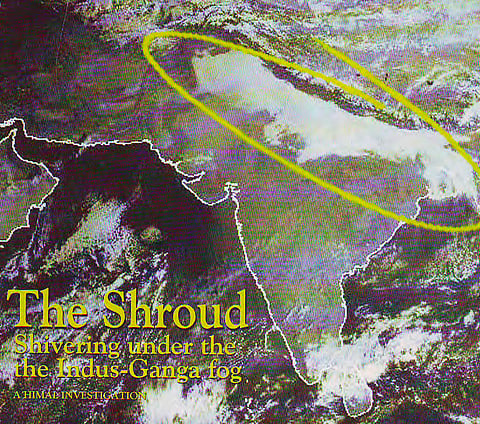
The dark white shroud: Shivering under the Indus-Ganga fog
In the winter of 2002-03, a protracted fog hugged the ground of the Indus and Ganga plains in the north and east of the Subcontinent for approximately 45 days. The resultant seet lahar (translated as 'cold wave') of December and January condemned 500 million people, living in a swathe of territory from Rawalpindi to Rangpur, to a sun-starved and frigid existence.
The fog disrupted life beyond just upsetting local airline schedules and delaying trains. In this, one of the most fertile belts of the world – the tropical and semi-tropical northern half of South Asia – lives a large section of global humanity, mostly in poverty. And it was exposed – under-clothed, undernourished – in the millions, to temperatures in the low single digits. The fog and the accompanying cold of the winter just passed struck a bitter blow.